1N5407 Pinout, Description, Equivalents, Applications, Features and More
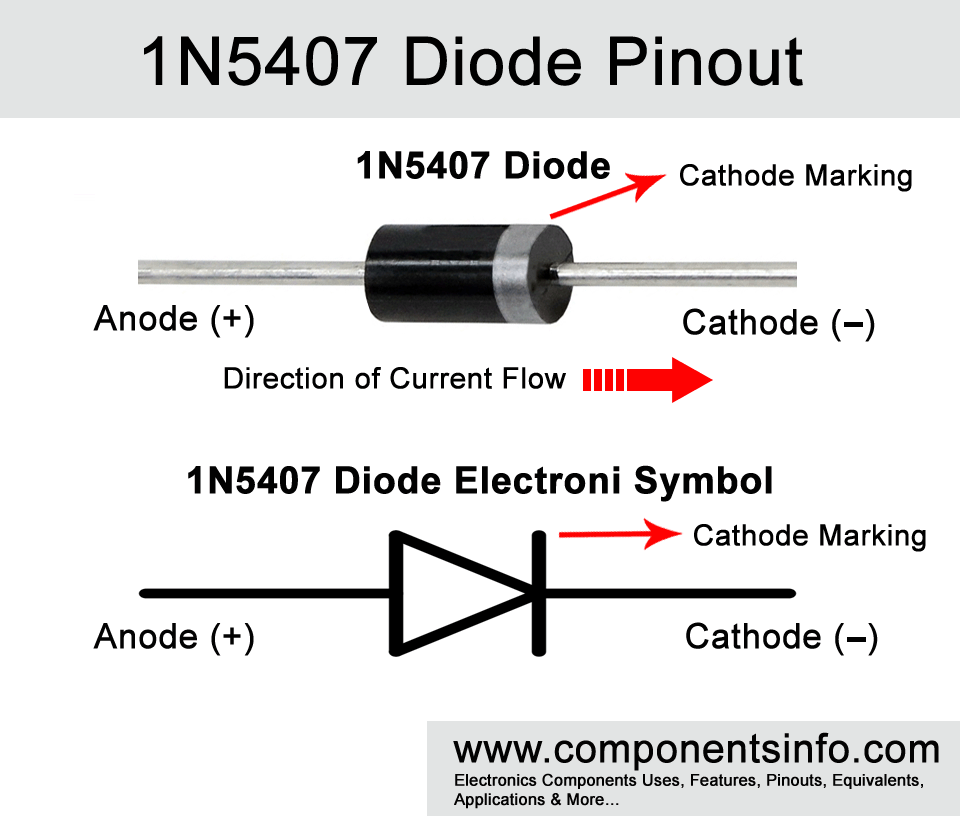
In this post we are going to study 1N5407 diode. It is a rectifier diode with high current capabilities. The post contains 1N5407 pinout, description, equivalents, applications, features, and details about this diode.
Features / Technical Specifications
- Package Type: Available in DO-201
- Diode Type: Rectifier Diode for General Purpose Applications
- Max Repetitive Reverse Voltage is: 800 Volts
- Average Rectified Fwd Current: 3000mA Or 3A
- Non-repetitive Max Fwd Current: 200A
- Max Reverse Current is: 10uA
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: -65 to +175 Centigrade
1N5407 Replacement and Equivalent
You can replace 1N5407 with the other diodes of its series but it is important to check the required voltage load of the circuit you are using it in, for example, if you are using it in a circuit or with a load that requires under 50V then you can replace it with any diode of the series but it the voltage requirements are above 50V and under 100V then you cannot replace it with 1N5400 but you can use 1N54001 and above. Same as when your load requirements are above 100V and below 200V then you cannot replace it with 1N5400 and 1N5401 but all the other diodes of the series because they have higher peak repetitive reverse voltage.
Other possible equivalents are P300M, CR3-100, CR3-120, G3M, FR307, FR607, HER508, and V3510.
1N5407 Diode Explained / Description
1N5407 is a rectifier diode available in DO-201 package. This diode is manufactured by several manufacturers and can be easily found. It is a diode of the 1N540X series which contains other diodes such as 1N5400, 1N5401, 1N5402, 1N5404, 1N545, 1N546 and 1N548. All the didoes in this series are almost same but there is only one noticeable difference which is their “Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage” which is very important to check. The Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage is a value that determines how much load a diode is capable to drive. So when using in a circuit it is important to check how much current your load requires according to this info you can select a suitable diode.
Coming back to the 1N5407 diode, the diode has many features such as high current of up to 3.0A, “High Surge Current Capability” means that the diode is capable of handling high voltage spikes. Moreover, it also has low leakage, leakage means when the diode is in off state there’s still a small amount of current that passes through the diode which is called leakage. There are different cons of leakage current such as it wastes power so if it is used in a portable or battery operated application then the battery will be drained fast. The leakage current also causes low accuracy in sensor circuits and also causes noise in some sensitive applications.
Where We Can Use It
It is a rectifier diode so its main application is to be used as a rectifier so it can be used in power supplies, voltage boosters, battery chargers, inverters, etc. Other than that it can also be used for other purposes such as for blocking current, blocking voltage spikes, etc.
Applications
Voltage Doubler Circuits
Power Supplies
Adapters
Rectification Circuits
Battery Chargers
Blocking voltage and current in any desired direction
Components Protection Purposes
AC to DC converters
Safe Operating Guidelines / Absolute Maximum Ratings
Here are the safe operating guidelines you should take into consideration when using this diode in your design or circuit.
- First of all, it is important to not use it on its absolute maximum ratings and stay 20% below from these absolute maximum ratings.
- Such as the maximum max repetitive reverse voltage of the diode is 800V so you have to stay under 640V or you have to drive load under 640V.
- The max average rectified forward current is 3.0A, therefore, do not drive load of more than 2.4A.
- Lastly always store or operate the device under the recommended temperature which is from -65°C to +175°C.
1N5406 Datasheet :
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the link below in your browser.
https://z3d9b7u8.stackpathcdn.com/pdf-down/1/N/5/1N5400-Diodes.pdf