2N5321 Transistor Pinout, Equivalents, Uses, Features, How to use, Safe Operating Guidelines and More
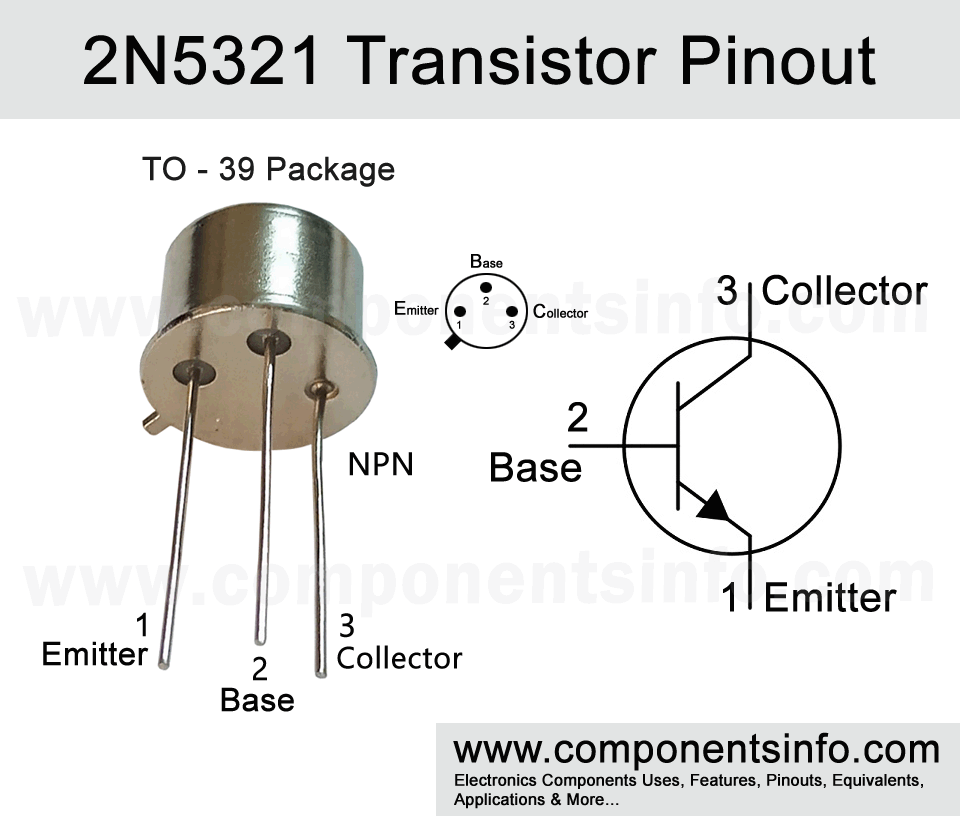
2N5321 is a metal case NPN transistor available in TO-39 package. It is a high voltage medium power transistor designed to be used in general purpose applications. In this post we are going to discuss 2N5321 transistor pinout, equivalents, uses, features, how to use, safe operating guidelines and more.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
- Package Type: TO-39
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 2A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 75V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 75V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Power Dissipation (PD): 10W
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 50 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 250
- Max Storage, Operating & Junction temperature range: -65 °C to +200 °C
PNP Complementary:
PNP Complementary of 2N5321 is 2N5323
Replacement and Equivalent:
2N5154, 2N5320
2N5321 Transistor Explained / Description:
2N5321 is an NPN metal case transistor available in TO-39 package. One of the main benefit of these metal case transistors are their wide temperature range that is from -65°C to +200 °C. Other features this transistor has are transition frequency of 50MHz, DC current gain of upto 250, power dissipation of 10W. All these features make it a good device to use in variety of general purpose switching and amplifier applications.
The absolute maximum ratings of the transistor are collector-emitter voltage of 75V, continuous collector current is 2A, collector-base voltage of 75V, emitter-base voltage is 5V, power dissipation of 10W (also mentioned above) and storage, operating and junction temperature range is from -65°C above +200 °C.
Looking at the pin layout of the transistor the first pin is Emitter, second pin is Base and the third pin is Collector. The transistor is designed to be used in switching applications but can also be used in wide variety of other general purpose applications such as amplification, motor driving, etc.
How to Use The Transistor:
We are not mentioning here the full circuits with all required passive components and showing how to use the transistor as a switch or amplifier, if you want the circuits then you can search online there are thousands of free circuits are available but we are only providing the basic concept of how to use the transistor as a switch and amplifier. To use the transistor as a switch connect the emitter pin with the ground, provide signals to the base pin (Signals from which you want to control the load) and connect the load negative wire with the collector pin and positive wire of the load will be connected with the positive rail.
For using the transistor as an amplifier the emitter pin will be connected with the negative rail of the circuit, the signal you want to amplify will be providing to the base pin and the amplified signal will be received from the collector pin. Now to further amplify or enhance the output of the transistor you can fed the amplified signal to other circuit for further enhancement or you can also connect the speaker or sound device between the collector and the emitter pin.
Applications:
Motors Control
Power supply
Switching circuits
Audio amplifier circuits
Voltage Regulator
Safe Operating Guidelines:
Here are some safe operating guidelines to use the transistor.
- Always use the transistor 20% below from the absolute maximum ratings.
- The maximum collector-emitter voltage is 75V but according to the above 20% rule we will not drive load of more than 60V.
- The maximum collector current is 2A but same as above we will not drive load of more than 1.6A.
- A heatsink will be required with the transistor.
- The storage and operating temperature should be between -65°C to +200 °C.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/68/2n5320-5323-1652634.pdf