BD161 Transistor Pinout, Equivalent, Applications, Features, Safe Operating Guidelines and More
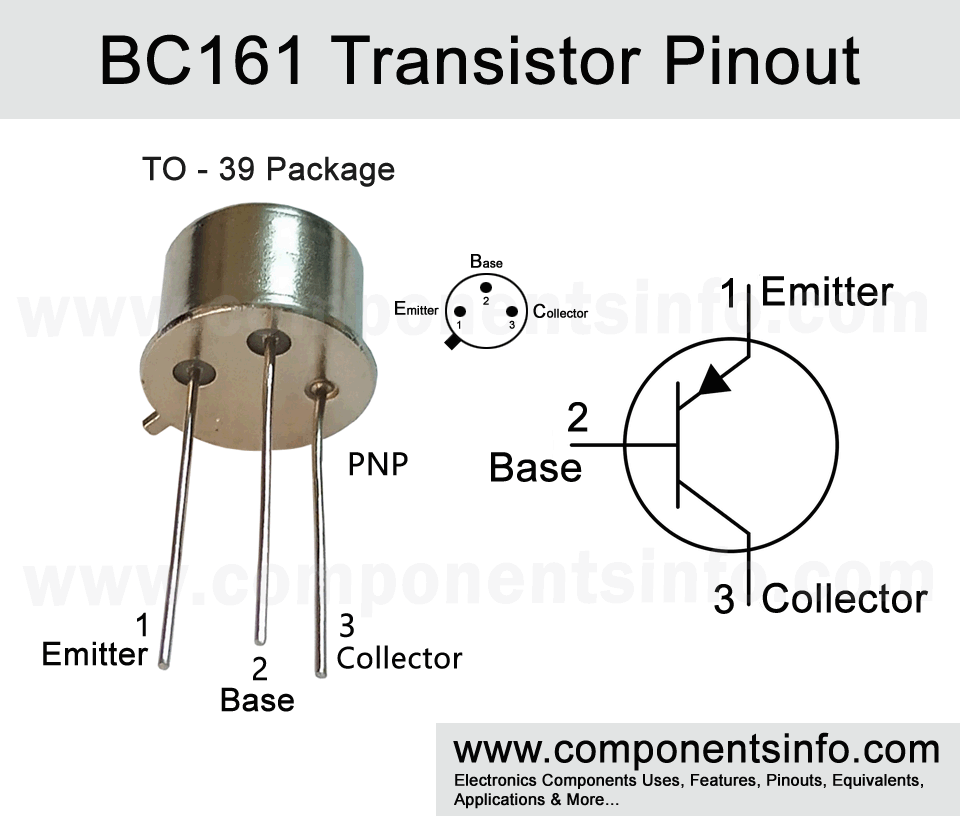
BC161 is a general purpose transistor available in TO-39 package. In this post we are going to understand BD161 transistor pinout, equivalent, applications, features, safe operating guidelines and other important details.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
- Package Type: TO-39
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Max Collector Current(IC): 1A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): -60V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): -60V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Total Power Dissipation (PD): 3.7W
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 50 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 250
- Max Storage, Operating & Junction temperature range: -65 °C to +200 °C
NPN Complementary:
NPN Complementary of BC161 is BC141
Replacement and Equivalent:
2N5153, BC461
BC161 Transistor Explained / Description:
BC161 is a TO-39 package PNP transistor designed to be used in general purpose applications. The transistor is having some good features which are max load voltage driving capacity is 60V, max load current it can drive is 1A, metal package, good DC current gain, and availability of a complimentary transistor.
Looking at the absolute max rating of the transistor the collector-emitter voltage is -60V, collector current is 1A, collector-base voltage is -60V, emitter-base voltage is 5V, total power dissipation is 3.7W and max storage and operating junction temperature is from -65 °C to +200 °C.
The transistor is designed for general purpose application so it can be used in wide variety of applications. The detailed list of its applications can be found under the “Applications” heading below.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
The transistor is designed to be used in general purpose applications such as audio and related applications, switching, controllers etc.
To use the transistor as a switch apply signal through a suitable resistor (Signal from which you want to control the transistor) to its base. Connect its emitter with the positive rail of the circuit and collector with the positive connection of the load and the negative connection of the load will be connected with the negative rail or ground of the circuit.
To use the transistor as an amplifier apply the signal you want to amplify to its base through a suitable capacitor and two resistor biasing network. Now emitter pin will be connected with the positive rail of the circuit and collector will be connected to the negative rail of the circuit through a load resistor. The amplified output will be taken from the connection point of transistor collector pin and load resistor.
Applications:
Switching circuits
Audio amplifier circuits
Audio Frequency Driver Circuits
Audio Output Stages
Voltage Regulator
Motors Control
Safe Operating Guidelines:
Here are some safe operating guidelines to use the transistor.
- Always use the transistor 20% below from its absolute maximum ratings.
- So the max collector current is 1A but by following the 20% rule we will only use 800mA for safe operation.
- The max collector-emitter voltage is 60V but by following the 20% rule we will only use 48V max.
- Always use a suitable heatsink
- And do not expose to temperatures below -65°C and above 200 °C.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://www.alldatasheet.com/datasheet-pdf/view/16091/PHILIPS/BC161.html