BD536 Transistor Pinout, Applications, Equivalent, Features, Safe Operating Guidelines and More
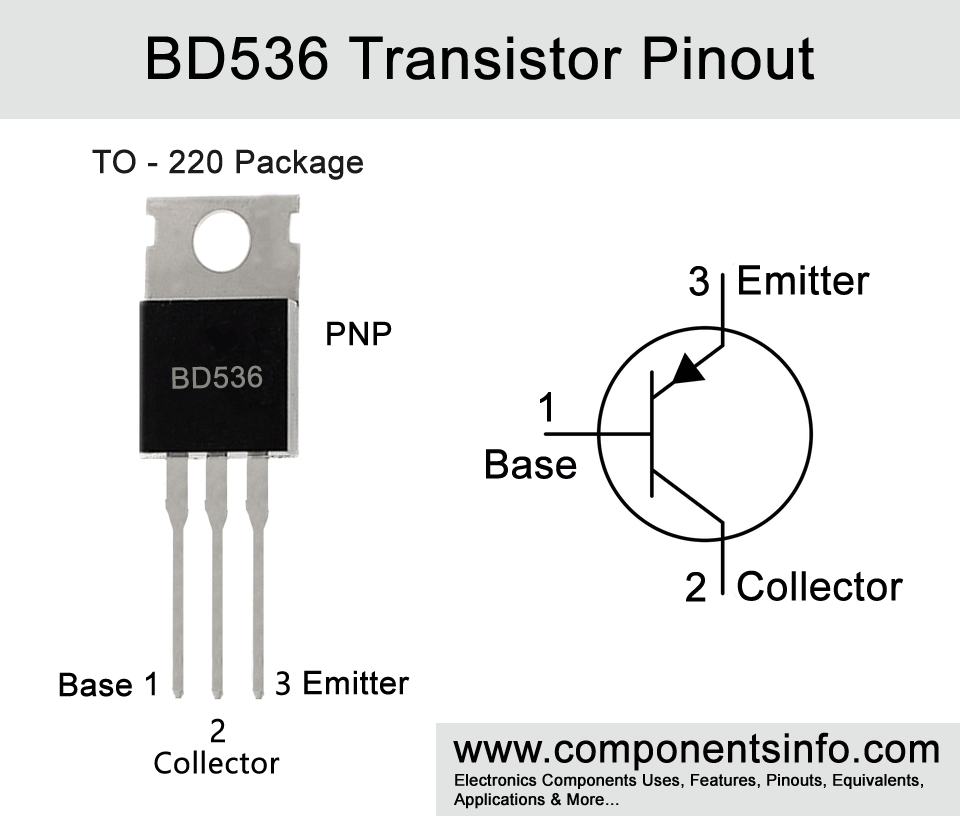
BD536 is a medium power PNP transistor available in TO-220 package. Today we will discuss BD536 transistor pinout, applications, equivalent, features, safe operating guidelines and more.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
- Package Type: TO-220
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Max Collector Current(IC): -8A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): -60V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): -5V
- Max Base Current (IB): -1A
- Max Collector Power Dissipation (Pc): 50W
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 40
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: –65 to +150 Centigrade
NPN Complementary:
NPN Complementary of BD536 is BD535
Replacement and Equivalent:
BDT86, BDT82, BDT64A/B/C, 2SB951, 2SB882, 2SB1225, TIP137, TIP136, TIP135, TIP107, TIP106, TIP105, MJE15029, BDX54C, BDX54A, BDX34/A/B/C, BDW94A/B/C, BDW74A/B/C, BDW48, BDW47, BDW46, BD538, 2SA1744, 2SA1743, 2SA1471, 2SA1452, 2SA1291
BD536 Transistor Explained / Description:
BD536 is a PNP transistor available in TO-220 package, designed to be used in switching and amplifier applications. It is a transistor of BD53X series which also contains other transistors such as BD534 and BD538. There is also complimentary of these transistors which are BD533, BD535 and BD537.
Looking at the pin layout of the transistor the first pin (Pin1) is base, second pin (Pin2) is collector and the third pin (Pin3) is emitter.
The absolute maximum ratings of the transistor are as follows: The collector-emitter voltage is -60V, collector-base voltage is also -60V, collector current is -8A, emitter-base voltage is -5V, base current is -1A, collector dissipation is 50W, junction temperature is 150°C and storage temperature is -60°C to 150°C.
Some electrical characteristics of the transistor are DC current gain of 40, typical and max collector-emitter saturation voltage is -0.8, and transition frequency is 3MHz to 12MHz.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
As mentioned above BD536 transistor is designed to be used in switching and amplifier applications due to which it can be used in a variety of these applications, the detailed list of its applications are listed below under the “Applications” heading.
For using the transistor as a switch apply the signal to its base through a suitable base resistor. Connect the emitter with the positive supply of the circuit and connect the collector of the transistor with the positive connection of the load and the negative connection of the load will be connected with the ground. To use the transistor as an amplifier here is a simple guide to do this. First apply the signal you want to amplify to the base of the transistor through a coupling capacitor, connect two resistors with the base, and connect one resistor other wire with the positive rail of the circuit and another resistor other wire with the negative rail of the circuit, connect the emitter of the transistor through a 1.2k resistor with the positive rail of the circuit and connect the collector of the transistor through a 5.1k resistor with the negative rail of the circuit. Now connect a 100uF capacitor positive lead with the collector of the transistor and negative lead with a speaker. Also, use a 1K resistor between 100uF capacitor’s negative connection and the negative rail of the circuit.
Applications:
Power Supplies
Audio Amplifiers
Voltage regulators
Relay Drivers
Motor Drivers
Switching Circuits
Audio amplifier driver stages
Driving load of upto 2A
Safe Operating Guidelines:
Here are the safe operating guidelines of the transistor.
- For safe operating always use the transistor at least 20% below from its absolute maximum ratings. This ensures reliable and long term performance of the transistor.
- According to the above 20% rule, we will calculate the collector current of the transistor accordingly. The maximum collector current of the transistor is -8A but we will not drive load of more than 6.4A.
- Same as in collector-emitter voltage the maximum collector-emitter voltage is -60V but will not drive load of more than 48V.
- Always use a proper heatsink with the transistor.
- Check the pin layout before placing it in the circuit.
- Store or operate the transistor at temperatures above -65°C and below 150°C.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://eu.mouser.com/datasheet/2/389/stmicroelectronics_cd00000915-1204519.pdf