BD711 Transistor Pinout, Equivalents, Applications, Features and Other Info
If you are looking for a transistor that can handle up to 12 amps of continuous collector current and up to 100V of collector-emitter voltage then the BD711, could be a good choice. This article contains all the details about BD711 transistor such as its pinout, equivalents, applications, features, where and how to use and other useful information about this device.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
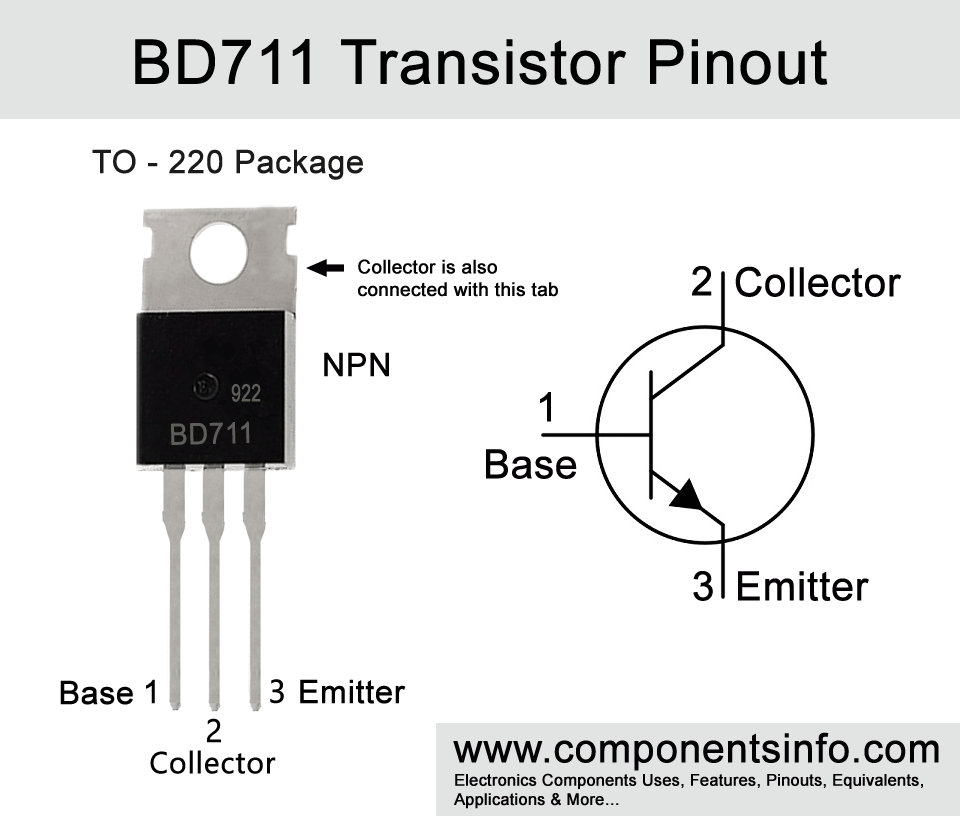
- Package Type: TO-220
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 12A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 100V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Max Base Current (IB): 5A
- Max Collector Power Dissipation (Pc): 75W
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 15 to 150
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: –65 to +150 Centigrade
PNP Complementary:
PNP Complementary of BD711 is BD712
Replacement and Equivalent:
NTE2343, ECG2343, BDW42G, 2SD2639
BD711 Transistor Explained / Description:
The BD711 is an NPN power transistor available in a TO-220 package. It is a transistor of the BD70X series which also includes other transistors such as BD707 and BD709. There is also a complementary series of these transistors such as BD708 which is complementary to BD707, BD710 which is complementary to BD709 and BD712 is complementary to BD711.
The pin layout is as follows: The first pin is Base, Second pin is Collector that is also connected to the Tab or mounting base of the transistor and the third pin is Emitter.
The transistor is designed to be used in switching and power linear applications due to which it can be used in variety of these type of applications.
Now looking at the absolute maximum ratings of the transistor the maximum collector current is 12A, max collector-emitter voltage is 100V, max base current is 5A, max emitter-base voltage is 5V, max collector power dissipation is 75W, max storage temperature is -65°C to 150°C and max junction temperature is 150°C.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
As mentioned above BD711 is designed to be used in switching and power linear applications. The transistor has quite good specs such as its 12A of current capacity, 100V of collector-emitter voltage and other features making it a robust device and makes it capable to use in variety of electronic applications such as power supplies, power amplifiers, motor control circuits, switching regulators, etc.
Here is a short guide on how to use the transistor:
The base pin of the transistor controls the output of the transistor. By applying small amount of current to the base we can control larger amount of current that that goes from collector to emitter of the transistor.
The Collector will be connected to the negative connection of the load and the positive connection of the load will be connected with the positive supply of the circuit.
The emitter pin is connected to the ground or negative supply in the majority of circuits.
Applications:
DC-DC Converters
Battery Charger Circuits
Motor Driver Circuits
Lighting Control Circuits
Power Supplies
Audio Amplifiers
Voltage regulators
Safe Operating Guidelines:
Here are the safe operating guidelines of the transistor.
- Do not use the transistor to its absolute maximum ratings and always stay 20% below from these ratings.
- The maximum collector current is 12A but we will only use the 80% of the total capacity that is 9.6A.
- The maximum collector-emitter voltage is 100V but we will only drive load under 80V.
- Check the pin layout before placing the transistor in the circuit.
- Use a suitable heatsink so it can fully dissipate the internal heat of the transistor.
- Always store or operate the transistor at temperatures above -65°C and below 150°C.
Datasheet:
To see the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://pdf1.alldatasheetde.com/datasheet-pdf/view/619472/NJSEMI/BD711.html