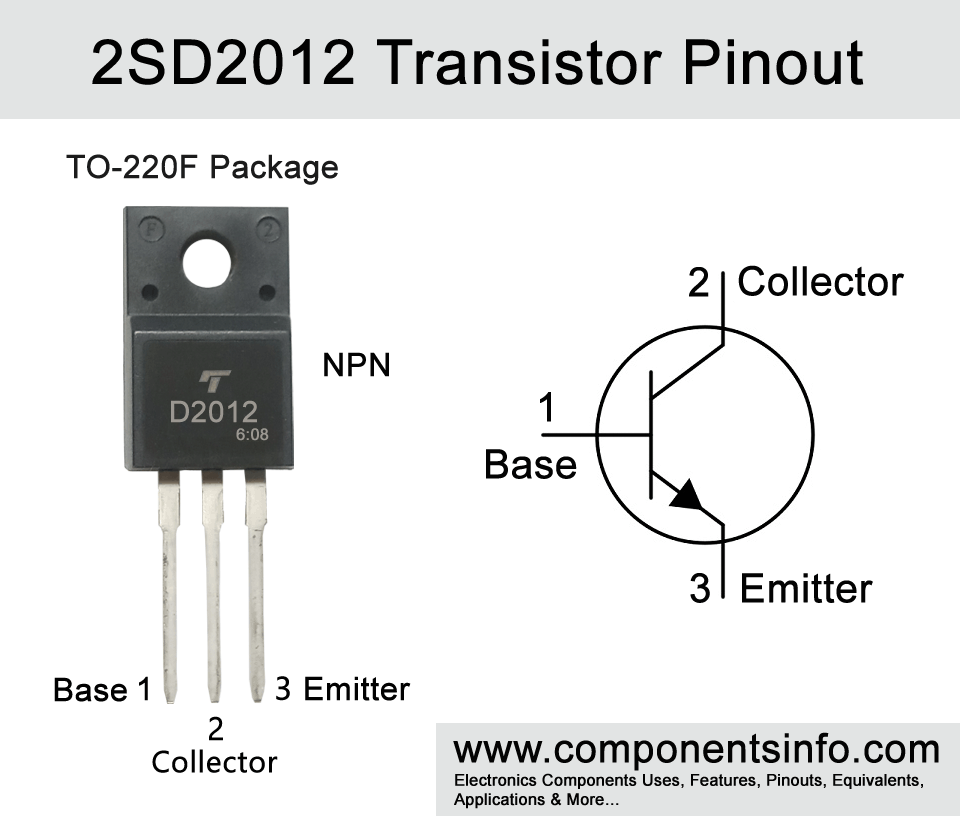
D2012 Transistor Pinout, Features, Applications, Equivalents and Other Information
D2012 is a Bipolar junction transistor designed for audio applications. This post describes the D2012 transistor pinout, features, applications, equivalents, and other information about this device.
Features / Technical Specifications:
- Package Type: TO-220F
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 3A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 60V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 60V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VBE): 7V
- Max Collector Dissipation (Pc): 25W
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 3 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 100 to 320
- Max Storage, Operating & Junction temperature range: -55 to +150 Centigrade
Replacement and Equivalent:
2SD1157, 2SD1122, 2SD1113, 2SD1115, 2SC4496, 2SC2438, 2SC4494, 2SC4353, 2SC2491, 2SC4055, 2SC2867, 2SC2963, 2SC2963
2SD2012 Transistors Explained / Description:
D2012 is an NPN transistor available in TO-220F package. The transistor is mainly designed for audio frequency power amplification purposes but can also be used in other audio related applications and also in switching applications.
The transistor has a low saturation voltage of 0.4V (Typ) and high power dissipation of 25W. Looking at the absolute maximum ratings of the transistor the collector to base voltage of the transistor is 60V, collector to emitter voltage is 60V, emitter to base voltage is 7V, the Collector current is 3A, Base Current (IB) is 0.5A and the collector power dissipation is 25 Watts. The absolute maxim rating is the maximum rating that can be achieved with the transistor but it is not a good practice to use the transistor to its absolute maximum ratings and it is suggested to use it at least 20% below from these ratings. Using any transistor to its absolute maximum ratings may damage the transistor, decrease its performance or make it unreliable to use for a long time in your circuits or design.
The electrical characteristics show how a transistor will perform in an electronic circuit when a signal is applied. The electrical characteristics of D2012 transistor are as follows:
The emitter cutoff current is 100uA, the collector cutoff current is also 100uA, and DC current gain is 100 to 320. Moreover, the transistor also features a very low collector to emitter saturation voltage that is 0.4V (Typ), the transition frequency is 3MHz and the collector output capacitance is 35pF.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
The transistor is designed for audio frequency power amplifier circuits but it can also be used for other purposes such as for switching, controlling of electrical current, voltage regulation circuits etc. The detail list of its applications can be found below. Additionally, it is a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) so the using procedure of this transistor is almost same as we use any other BJT transistor.
Applications:
Audio amplifiers:
It can be used in high power audio amplifiers to boost audio to a higher level.
Switching:
Whether it is designed to use in audio applications but it can also be used in switching applications and drive load of upto 3A and due to its low collector to emitter saturation it can also be used in applications where low voltage activation is required.
Motor Control:
It can also be used in motor applications to control a DC motor under 3A.
Power Supplies:
2SD2012 can also be used in power supply circuits.
Lighting Applications:
It can also be used to control the light (brightness) in variety of applications for example street lights, automobiles etc.
Safe Operating Guidelines
To safely operate the transistor it is suggested to always use it 20% below from its absolute maximum ratings.
- The maximum collector to emitter voltage is 60V therefore do not drive load of more than 48V.
- The max collector current of the transistor is 3A so do not drive load of more than 2.4A.
- And always store or operate the transistor at temperatures above -55°C and below +150 °C.
Datasheet:
To Download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://z3d9b7u8.stackpathcdn.com/pdf-down/D/2/0/D2012_ToshibaSemiconductor.pdf