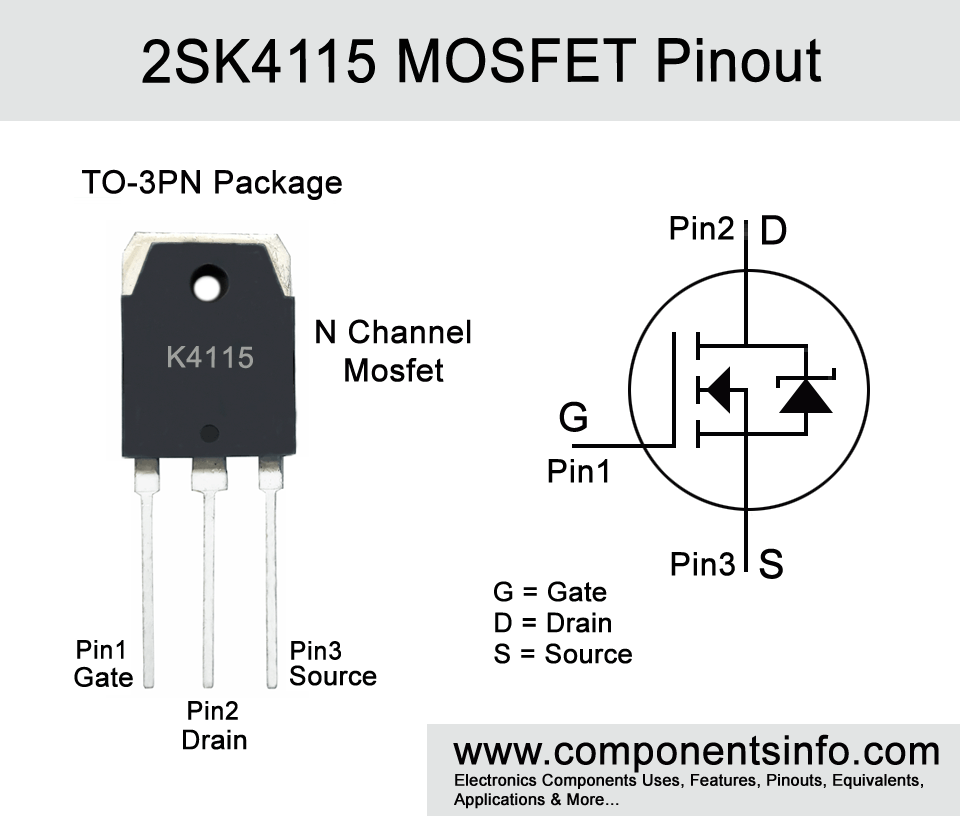
K4115 MOSFET Pinout, Equivalent, Features, Applications, Where and How to Use and More
Are you searching for additional information on 2sk4115 MOSFET for some reason or looking for its alternative use in the circuit you are working on then you have come to the right place. This page contains all the information about this transistor such as K4115 pinout, equivalent, features, applications, where and how to use and many other useful information.
Max Ratings & Technical Specifications:
- Package Type: TO-220AB
- Transistor Type: P Channel
- Max Voltage Applied From Drain to Source: 900V
- Max Drain to Gate Voltage: 900V
- Max Gate to Source Voltage Should Be: ±30V
- Max Continues Drain Current is : 7A
- Max Pulsed Drain Current is: 21A
- Max Power Dissipation is: 150W
- Drain to Source Resistance in ON State (RDS on): 1.66 Ω (Typical)
- Max Storage Operating & Junction temperature is: -55 to +150 Centigrade
Replacement and Equivalent:
2SK4207
2SK4115 Transistor Explained / Description:
K4115 full part number 2SK4115 is an N Channel silicon MOSFET available in TO-3PN package. It has many features such as:
Enhancement Mode:
Mean that the transistor can turn on with a very low amount of voltage.
Low Drain to Source ON Resistance (RDS(ON)):
This means that when the MOSFET is in ON condition it has very low resistance when electricity passes through its drain to source.
100% Avalanche Tested:
100% avalanche tested means this MOSFET is already tested with sudden voltage spikes and it has proven to pass the test without getting damage.
Low Leakage Current:
Means that this transistor not allow the flow of electricity in off mode. This is important when you want to make power efficient circuits.
looking at the absolute maximum ratings of the MOSFET, the drain to source voltage is 900V, drain current is 7A, pulsed drain current is 21A, drain to gate voltage is also 900V, gate to source voltage is ±30 and drain power dissipation is 150W.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
The MOSFET can be used in control circuits, power circuits, charging circuits, amplifier circuits, etc. The detailed list can be found below under it Applications.
The MOSFETs are voltage controlled devices so they can be controlled by providing voltage to their gate so they can drive the output load, different MOSFETs have different gate voltage requirements to drive the output load. To use this MOSFET connect its gate to the input signal, its source to the negative supply and its drain pin to the negative of load and the load positive will be connected with the positive supply of the circuits. Also note that using a resistor between the input signal and gate of the MOSFET is important. On this link you will find the details about MOSFET gate resistor. https://www.build-electronic-circuits.com/mosfet-gate-resistor/
Applications:
Switching Regulators
BMS Circuits
LED Driver Circuits
Power Amplifiers
Motor Driver applications
Power Management
Switch Mode Power Supplies
High Voltage Applications
Small UPS Circuits
Audio Amplifier Circuits
Battery Chargers Circuits
Safe Operating Guidelines
For safe operation it is suggested to not use the MOSFET to its absolute max ratings and stay at least 20% below from its max ratings.
- Max drain to source voltage is 900V therefore do not drive load of more than 720V.
- Max drain to gate voltage should also be under 720V.
- Max gate to source voltage must be under ±30V
- The max continuous drain current is 7A therefore do not drive load of more than 5.6A.
- Use a suitable heatsink with the MOSFET.
- Always store or operate the MOSFET at temperature below -55°C and above +150 °C.
.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://z3d9b7u8.stackpathcdn.com/pdf-down/K/4/1/K4115_ToshibaSemiconductor.pdf